“Money is money because almost everyone believes it’s money”
- What is Money
- Evolution of Money
- Functions of Money
- Measures of Money
- Money Multiplier
- Cryptocurrency
- CBDC(eRupee)
What is Money?
Money has been defined differently by different economists. But the most acceptable definition of money can be stated in terms of all the functions of money.
Money is anything which is generally accepted as a means of exchange, a measure and store of value and which also acts as standard of deferred payments.
Everybody needs money for various purposes starting from day to day transactions to saving for future. But if one goes back to history, will find that before money came into existence there was barter system to facilitate transactions among individuals in the society. With development of civilization over time, barter system lost its ground and was replaced by money.
Evolution of Money:
At our very first stop we find ourselves in the times of the caveman. Somewhere in those ancient ages people started to find that they can exchange something that is theirs for something that is someone else’s. This is called Barter System.
Quite early on, though commodity money started to become widespread. Commodity money is money whose value comes from a commodity of which it is made. Commodity money consists of objects that have value in themselves as well as value in their use as money. This commodity money was accepted by everybody to be of high value. But it had to be of stable value, divisible and easy to handle. Cloth, sheep, cows, even salt was used in some places.
The next stop is coinage. This is just like commodity money, but the commodity is the metal that the money is made of. Their metal content was always the same (well, legally anyway) so it could be used to exchange in a uniform way.
Only a small step from here is precious metal based money. Red gold was main payment method for about 2500 years! You were actually, in practice able to pay with gold coins until about 1910, and it stayed the basis for the international monetary systems.
During this time another type of money was evolving, called “representative money”. This is the money we use today. The actual material of the money is not valuable, it has a market value. This currency was backed by the government or a bank, who promised to redeem the representative money for a given weight of precious material, such as silver or gold.
Another type of money is “fiat money” (yes, like the car). This is representative money, which is not backed by the government. It is given value by decree. This has been used by many governments in crisis, or in wars. In 1971 the US switched to fiat money, which was some problem for Western countries whose currencies were fixed to the dollar.
The modern state of money, which is actually not easy to distinguish from other types, is “credit money”. It is any future monetary claim (borrowing and paying back) against an individual that can be used to buy goods and services.
Today money is no longer gold based, because increasing demand cannot be fulfilled by gold. Credit money is the most widespread, but now electronic money is being revolutionized and may take over quickly. This is not exactly credit money because it is not (or will not be) backed up by real money. It is sort of a mix between credit money and fiat money.
Legal Tender:
Fiduciary Money:
Q) Which one of the following statements correctly describes the meaning of legal tender money?
(a) The money which is tendered in courts of law to defray the fee of legal cases.
(b) The money which a creditor is under compulsion to accept in settlement of his claims.
(c) The bank money in the form of cheques, drafts, bills of exchange, etc.
(d) The metallic money in circulation in a country.
Functions of Money:
Supply of Money
In a modern economy money consists mainly of currency notes and coins issued by the monetary authority of the country. In India currency notes are issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which is the monetary authority in India. However, coins are issued by the Government of India.
Creation of Credit by Commercial Banks: Credit creation is one of the most important functions of a commercial bank. Banks create credit out of the deposits that is mobilized by them. Credit creation is also called money creation or deposit creation. Therefore, commercial banks are also known as creator of money or credit.
The process of credit/money creation: 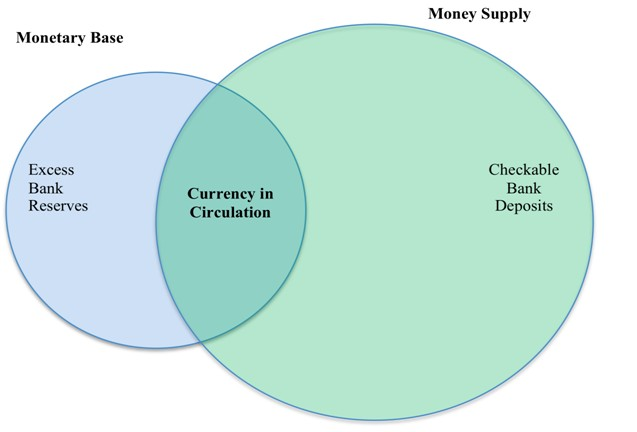
Money is not created by commercial banks by actually printing of notes or minting of coins. The money is created by granting loans and advances to public and making relevant entries into the books of accounts of the lending banks.
Loans are granted out of the deposits received by the banks. Normally, the amount of loan granted by a bank is greater than the amount of deposits received by it. This is mainly because of the fact that when money is deposited by the depositors in a bank, the bank by its experience knows that not all the money would be withdrawn by the depositors at once at any point of time.
This peculiar habit of the depositors leaves the bank with huge amount of surplus fund which in turn is used to create loans by the banks. The banks keep certain proportion of its total deposits in form of cash to honour the demand of its customers.
Fractional Reserve System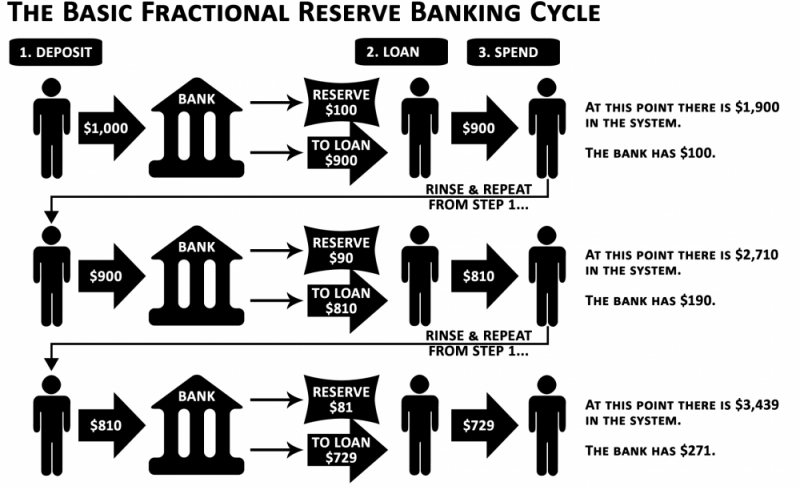
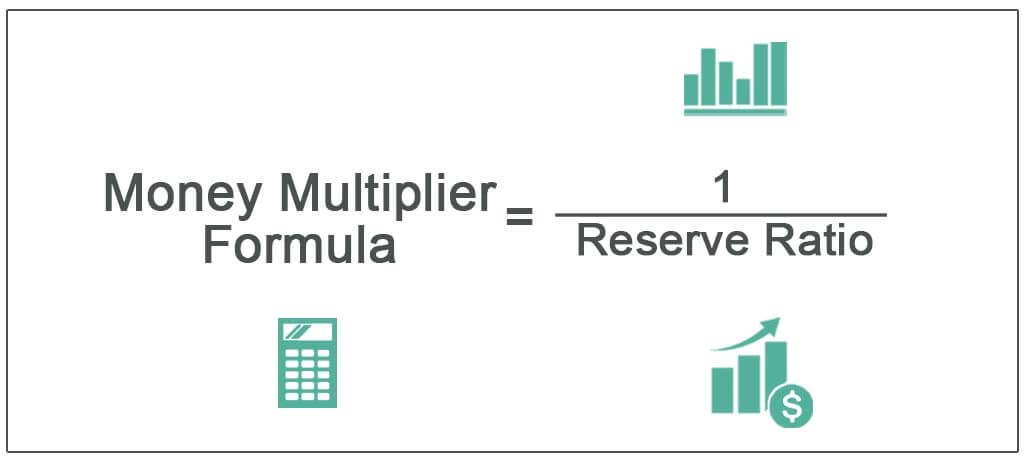
Money Multiplier:
Definition: It is the ratio of Broad money (M3) divided by Reserve Money (M0). It represents money supply as in, for each rupee of money of the Central Bank in India, how many rupees get generated in the Indian Economy. Every one rupee of central bank money in India is able to generate around 6 rupees of money supply in the economy. India’s ratio remains lower than that of Europe, but higher than that of the US.
Q) If you withdraw Rs. 1,00,000 in cash from your Demand Deposit Account at your bank, the immediate effect on aggregate money supply in the economy will be
(a) To reduce it by 1,00,000
(b) To increase it by approx. 1,00,000
(c) To increase it by more than 1,00,000
(d) To leave it unchanged
Its significance: A higher value for this ratio, called the money multiplier, indicates that the banking system generates a higher money supply out of money given by central bank. In India, the recent push to financial inclusion has led to people holding less cash in hand (relative to deposits) leading to an increase in the money multiplier.
A country’s money multiplier depends on two factors—how much individuals (and businesses) hold in cash and how much banks hold as reserves. The more individuals hold cash in hand, the less the banking system will be able to create money and hence a lower value for the multiplier. In other words, cash in hand acts as a leakage for the banking system.
Q) The money multiplier in an economy increases with which one of the following?
(a) Increase in the cash reserve ratio
(b) Increase in the banking habit of the population
(c) Increase in the statutory liquidity
(d) Increase in the population of the country
Similarly, reserves that banks hold with the central bank also amount to a leakage, which again reduces the money multiplier. It should be noted that central banks generally tell the banks to maintain a part of their deposits as reserves, called the cash reserve ratio. So in essence, it is only the excess reserves (that banks maintain over and above the central bank’s requirement) that constitute leakages.
Measures of Money:
Narrow and Broad Money
Money supply, like money demand, is a stock variable. The total stock of money in circulation among the public at a particular point of time is called money supply. RBI publishes figures for four alternative measures of money supply, viz. M1, M2, M3 and M4.
They are defined as follows:
M1 = CC + DD + OD
CC = Currency in Circulation
DD = Demand deposits with the banks
OD = Other deposits with RBI
M2 = M1 + Savings deposits with Post Office savings banks
“M1 and M2 are known as Narrow Money.”
M3 = M1 + Net time deposits of commercial banks
M4 = M3 + Total deposits with Post Office savings organisations (excluding National Savings Certificates)
“M3 and M4 are known as Broad Money.”
Where, CU is currency (notes plus coins) held by the public and DD is net demand deposits held by commercial banks. The word ‘net’ implies that only deposits of the public held by the banks are to be included in money supply.
The interbank deposits, which a commercial bank holds in other commercial banks, are not to be regarded as part of money supply. These gradations are in decreasing order of liquidity. M1 is most liquid and easiest for transactions whereas M4 is least liquid of all. M3 is the most commonly used measure of money supply. It is also known as “aggregate monetary resources”.
High Powered Money: The total liability of the monetary authority of the country, RBI, is called the monetary base or high powered money. It consists of currency (notes and coins in circulation with the public and vault cash of commercial banks) and deposits held by the Government of India and commercial banks with RBI.
Q) The sum of which of the following constitutes Broad Money in India?
1. Currency with the public
2. Demand deposits with banks.
3. Time deposits with banks
4. Other deposits with RBI
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1,2 and 3
(c) 1,2,3 and 4
(d) 1,2 and 4
Q) Consider the following:
1. Currency with the public
2. Demand deposits with banks
3. Time deposits with banks
Which of these are included in Broad Money in India?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
What Is Seigniorage?
Seigniorage is the difference between the face value of money, such as Rs.100, and the cost to produce it. In other words, the cost of producing a currency within a given economy or country is lower than the actual exchange value, which generally accrues to governments that mint the money.
If the seigniorage is positive, the government will make a profit; a negative seigniorage will result in a loss.
Understanding Seigniorage
Seigniorage is counted as revenue for a government when the money it creates is worth more than it costs to produce. This revenue is often used by governments to finance portions of their expenditures without having to collect taxes. If, for example, if it costs the government Rs.5 to produce Rs.500, the seigniorage is Rs.495, the difference between the two amounts. Seigniorage gives a country the potential to turn a profit when it produces money.
While the definition of seigniorage is most often the difference between the cost of printing new currency and the face value of that same currency, it is also the number of goods or services a government can acquire through the printing of new notes.
Soiled and Mutilated Notes
Clean Note Policy
Cryptocurrencies
A cryptocurrency is a form of digital money which is designed to work as a medium of exchange and uses a cryptography method to keep it secure the transaction.
Cryptocurrency uses the decentralized network. That means you don’t need any third party server like bank, government, other authorities to perform any type of transaction with the merchants.
Benefits of using cryptocurrency –
- Cryptocurrency, being as a decentralized network of the transaction. It is free from the eagle-eye of the third party server like banks, government, and other authority.
- As third party servers do not involve in any kind of decentralized transactions. It saves you from double spending which in turn saves you huge extra bucks which you used to pay as taxes, duties etc
- This technology completely eradicates the uncertainty of fraudulence, double dealing, embezzlement, and smuggling.
- Highly secured.
- No documentation/paper work.
- Saves time.
Problems of Using Cryptocurrency:
- There is some limitation that cryptocurrency presently faces some difficulties to adapt it completely.
- Like one’s digital fortune can be erased due to the computer crash, or that a virtual vault may be ransacked by a hacker – may be overcome in time through technological advances.
- This technology of cryptocurrency seems to be very beneficial which has so many pros that accompany along with.
- Researchers, institutions, and the government should have highly scrutiny over these issue of security of cryptocurrency.
So, that peoples can use the technology of digital cash system being Unperturbed.
Popular Cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin: Released in 2009 by someone under the alias Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is the most well-known of all cryptocurrencies. Despite the complicated technology behind it, payment via Bitcoin is simple. In a transaction, the buyer and seller utilize mobile wallets to send and receive payments. Although Bitcoin is widely recognized as pioneering, it is not without limitations. Not only is Bitcoin slower than some of its alternatives, but its functionality is also more limited.
Q) With reference to ‘Bitcoins’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Bitcoins are tracked by the Central Banks of the countries.
2. Anyone with a Bitcoin address can send and receive Bitcoins from anyone else with a Bitcoin address.
3. Online payments can be sent without either side knowing the identity of the other.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1,2 and 3
- Ether &Ethereum: Often used interchangeably, Ethereum is a platform that allows for relatively easy creation of smart contracts while Ether is a “token” used to enter into transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. Put simply, smart contracts are computer programs that can automatically execute the terms of a contract. They function similarly to the “IF (then)” Excel function: When a pre-programmed condition is triggered, the smart contract executes the corresponding contractual clause.
- Litecoin: Launched in 2011, Lite coin functions similarly to Bitcoin in that is also open sourced, decentralized, and backed by cryptography. However, it was intended to serve in a complementary role to Bitcoin, “the silver to Bitcoin’s gold.” Litecoin has a faster block generate rate and faster transaction confirmation.
- Dash: Released in 2014 as “Darkcoin,” Dash has since re-branded and offers more anonymity for its users due to its decentralized master code network. It utilizes something called a “Masternode” network which has a more robust foundation than Bitcoin.
- Zcash: Released in October 2016, Zcash is a relative newcomer in the space. However, there are claims that it is the first truly anonymous crypto currency in existence due to its employment of zero knowledge SNARKS, which involves no transaction records whatsoever. The technology ensures that, despite all the information being encrypted, it is still correct and that double spending is impossible.
- Monero: Monero possesses unique privacy properties. For example, Monero enables complete privacy by leveraging a technique called “ring signatures.” It’s become popular in the dark web black market, where users purchase everything from drugs to firearms.
Central Bank Digital Currency(CBDC)
Components of CBDC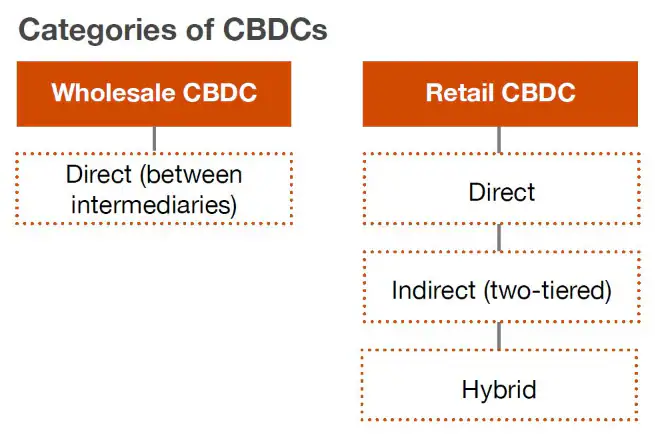 Benefits of CBDC
Benefits of CBDC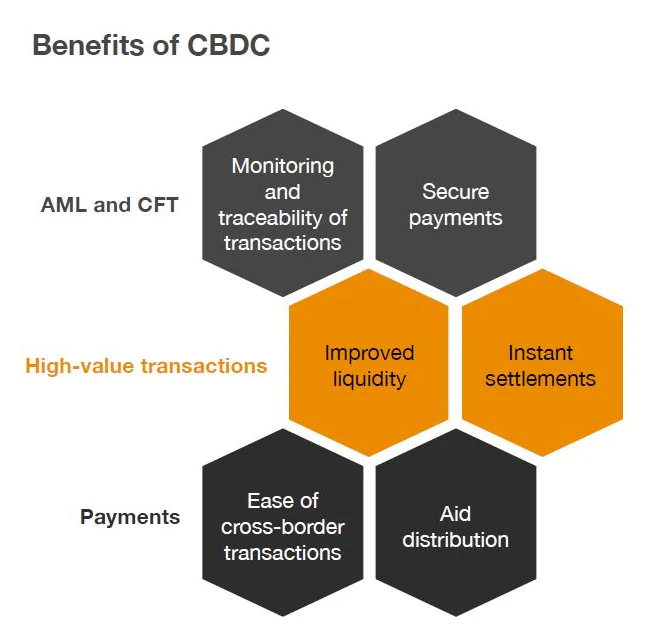
Pros and Cons of CBDC Financial System of India
Financial System of India